What is Content Security Policy (CSP)?
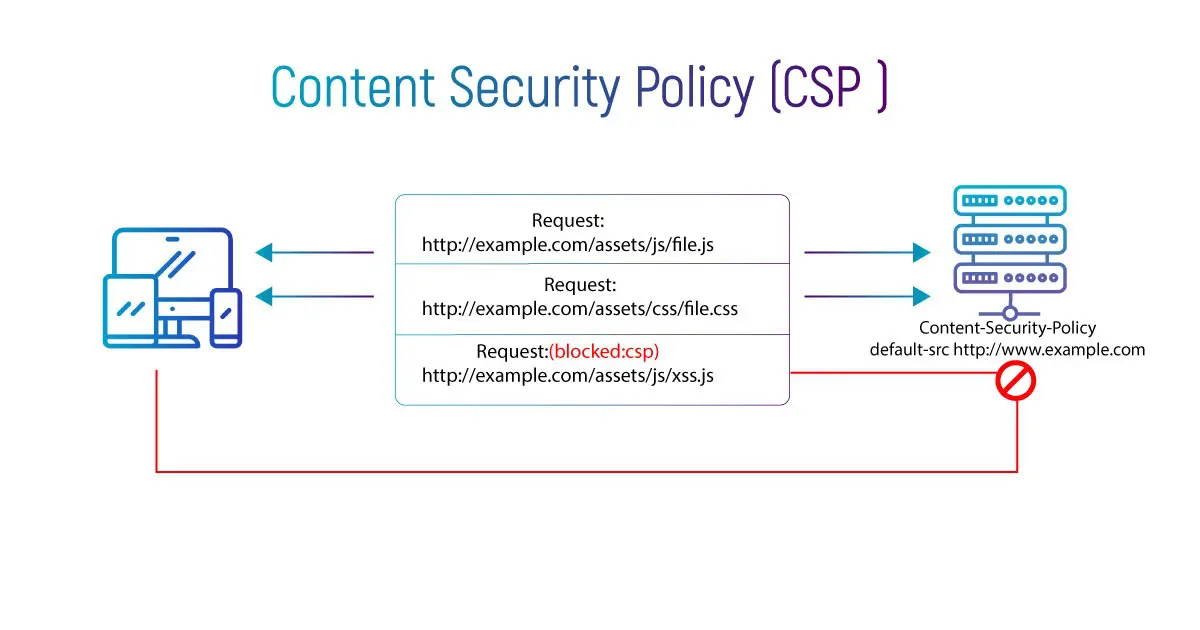
Content Security Policy (CSP) is an additional layer of security on the HTTP browser traffic to mitigate Cross-Site-Scripting (XSS), data injection attacks.
CSP is designed to be backwards compatible, i.e. when browsers do not support CSP, it defaults to the same-origin policy for web content.
Configuration
CSP configuration requires the web server to return the Content-Security-Policy HTTP header.
Content-Security-Policy: policy-directive; policy-directive
The primary objective of CSP is to prevent XSS. XSS exploits the browser’s trust in all the content being loaded by the document to inject malicious executable scripts. A CSP compatible browser only executes scripts and resource files specified by the policy directives in the CSP HTTP header.
Content-Security-Policy: default-src 'self'; img-src *; media-src prophaze.com *.prophaze.com; script-src js.prophaze.com
In this instance the web admin wants the default content to load from the website’s own origin (note ‘self’), images from anywhere on the internet (note wildcard ‘*’), media from prophaze.com and all its subdomains, and javascript from js.prophaze.com.
The web admin can also specify resources to specifically load over https.
Content-Security-Policy: default-src 'self' https://prophaze.com
For deployment purposes, CSP can be deployed in a report-only mode where by policy, any CSP violation is reported to the value specified in the header through a POST request.
Content-Security-Policy-Report-Only: to-test-policy
Content-Security-Policy: default-src 'self' https://prophaze.com; report-uri /dev/report-csp
In the above example, all violations will be reported to /dev/report-csp on origin.












